HTH
HTH یا مارپیچ-پیچ-مارپیچ (انگلیسی: Helix-turn-helix) یک موتیف ساختاری مهم در پروتئینهاست که قادر است به دیانای اتصال یابد.
| پروتئین تنظیمکننده HTH در باکتری، خانوادهٔ lysR | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| شناسهها | |||||||||
| نماد | HTH_1 | ||||||||
| پیفم | PF00126 | ||||||||
| پیفم clan | CL0123 | ||||||||
| اینترپرو | IPR000847 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00043 | ||||||||
| SCOPe | 1al3 / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
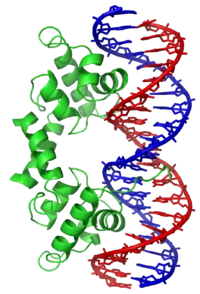
سرکوبگر λ در باکترویفاژ لامبدا از یک موتیف HTH (سمت چپ؛ سبز) برای اتصال به دیانای (سمتراست: آبی و قرمز) استفاده میکند.
این موتیف از دو مارپیچ آلفا تشکیل شده که توسط رشتهٔ کوتاهی از اسیدهای آمینه به هم متصل شدهاند و در بسیاری از پروتئینهایی که در تنظیم بیان ژن دخالت دارند، دیده میشود. این موتیف را نباید با موتیف دیگری به نام HLH اشتباه گرفت.[1]
این موتیفها بر اساس ساختار و نحوهٔ قرارگیری فضاییِ مارپیچِ حلزونیشکلشان به چند زیرگروه تقسیم میشوند:[2][3][4]
- دو حلقهای
- سه حلقهای
- چهار حلقهای
- بالدار
- متفرقه
جستارهای وابسته
منابع
- Brennan RG, Matthews BW (1989). "The helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif". J Biol Chem. 264 (4): 1903–6. PMID 2644244.
- Wintjens R, Rooman M (1996). "Structural classification of HTH DNA-binding domains and protein-DNA interaction modes". J Mol Biol. 262 (2): 294–313. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0514. PMID 8831795.
- Suzuki M, Brenner SE (1995). "Classification of multi-helical DNA-binding domains and application to predict the DBD structures of sigma factor, LysR, OmpR/PhoB, CENP-B, Rapl, and Xy1S/Ada/AraC". FEBS Lett. 372 (2–3): 215–21. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(95)00988-L. PMID 7556672.
- Aravind L, Anantharaman V, Balaji S, Babu MM, Iyer LM (2005). "The many faces of the helix-turn-helix domain: transcription regulation and beyond". FEMS Microbiol Rev. 29 (2): 231–62. doi:10.1016/j.femsre.2004.12.008. PMID 15808743.
- مشارکتکنندگان ویکیپدیا. «Helix-turn-helix». در دانشنامهٔ ویکیپدیای انگلیسی، بازبینیشده در ۲۰ دسامبر ۲۰۱۷.
بیشتر بخوانید
- Struhl K (1989). "Helix-turn-helix, zinc-finger, and leucine-zipper motifs for eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins". Trends Biochem Sci. 14 (4): 137–40. doi:10.1016/0968-0004(89)90145-X. PMID 2499084.
- Gajiwala KS, Burley SK (2000). "Winged helix proteins". Curr Opin Struct Biol. 10 (1): 110–6. PMID 10679470.
- Santos CL, Tavares F, Thioulouse J, Normand P (2009). "A phylogenomic analysis of bacterial helix-turn-helix transcription factors". FEMS Microbiol Rev. 33 (2): 411–29. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00154.x. PMID 19076237.
- Hoskisson PA, Rigali S (2009). "Chapter 1: Variation in form and function the helix-turn-helix regulators of the GntR superfamily". Adv Appl Microbiol. 69: 1–22. doi:10.1016/S0065-2164(09)69001-8. PMID 19729089.
- Brennan RG (1993). "The winged-helix DNA-binding motif: another helix-turn-helix takeoff". Cell. 74 (5): 773–6. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90456-Z. PMID 8374950.
- Huffman JL, Brennan RG (2002). "Prokaryotic transcription regulators: more than just the helix-turn-helix motif". Curr Opin Struct Biol. 12 (1): 98–106. doi:10.1016/s0959-440x(02)00295-6. PMID 11839496.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
