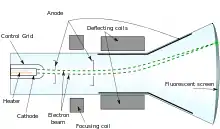
ابزار اندازهگیری
در علوم فیزیکی، تضمین کیفیت، مهندسی، اندازهگیری روشهایی برای بیانکنند و مقایسهٔ کمیت فیزیکی اجسام و پدیدههای دنیای واقعی هستند. برای تعریف اجسام و رویدادها به صورت استاندارد نیاز به استفاده از یکاها هست و روند اندازهگیری اعدادی را در اختیار میگذارد که مرتبط با موارد مورد مطالعه هستند و به یکای اندازهگیری اشاره دارند. ابزارهای اندازهگیری و روشهای آزمودن که روش استفاده از ابزارها را تعریف میکنند مقدار متوسط رابطهٔ بین عددها و یکاها را مشخص میکنند خطای ابزار و خطای عدم قطعیت در استفاده از ابزارهای اندازهگیری وجود دارد. دانشمندان و مهندسین و بهطور کلی انسانها از ابزارهای اندازهگیری مختلفی برای شرح محیط اطراف خوداستفاده میکنند که شامل سادهترین موارد مانند خطکش تا پیچیدهترین آنها مانند میکروسکوپ الکترونی و شتابدهنده ذرهای میشود. از ابزارهای مجازی برای توسعه ابزارهای اندازهگیری جدید استفاده میشود.

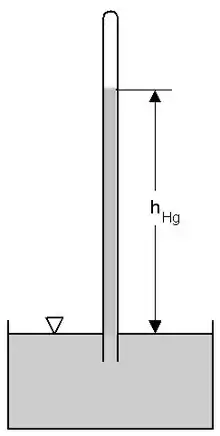
زمان
تعدادی از ابزارهای سنجش زمان به شرح زیر هستند
- ساعت اتمی
- گاهشماری
- کورنومتر, کورنوگراف
- ساعت
- زمانسنج تخممرغی
- ساعت
- ساعت شنی
- ساعت پاندولی
- ساعت رادیویی
- زمانسنجی رادیومتریک
- قدمشمار
- ساعت آفتابی
- تلسکوپ ترانزیتی
- ساعت آبی
تاریخچه تکنولوژی زمانسنجی
انرژی

Example: In a plant that furnishes نیروگاه تلمبه ذخیرهای, کار (فیزیک) and electrical work is done by machines like electric پمپs and مولد الکتریکیs. The pumped water stores mechanical work. The amount of energy put into the system equals the amount of energy which comes out of the system, less that amount of energy used to overcome اصطکاک.
Such examples suggested the derivation of some unifying concepts: Instead of discerning (transferred) forms of work or stored work, there has been introduced one single کمیت فیزیکی called energy. Energy is assumed to have substance-like qualities; energy can be apportioned and transferred. Energy cannot be created from nothing, or to be annihilated to nothing, thus energy becomes a conserved quantity, when properly balanced.
Describing the transfer of energy two dictions, two ways of wording are used:
(energy carriers exchanging energy) Physical interactions occur by carriers (linear momentum, electric charge, entropy) exchanging energy. For example, a generator transfers energy from angular momentum to electric charge.[1]
(حاملهای انرژیs transforming energy) Energy forms are transformed; for example انرژی مکانیکی into انرژی پتانسیل الکتریکی by a generator.[2]
Often the energy value results from multiplying two related quantities: (a generalized) potential (relative velocity, voltage, temperature difference) times some substance-like quantity (linear momentum, electrical charge, entropy). — Thus energy has to be measured by first choosing a carrier/form. The measurement usually happens indirectly, by obtaining two values (potential and substance-like quantity) and by multiplying their values. For the ranges of energy-values see: Orders of magnitude (energy)
Power (flux of energy)
A physical system that exchanges energy may be described by the amount of energy exchanged per time-زمان, also called power or شار of energy.
- (see any measurement device for power below)
Action
Action describes energy summed up over the time a process lasts (time انتگرال over energy). Its بعد is the same as that of an تکانه زاویهای.
- A phototube provides a voltage measurement which permits the calculation of the quantized action (ثابت پلانک) of light. Also see اثر فوتوالکتریک.
مکانیک
کمیتهای ابتدایی که در مکانیک کلاسیک- و مکانیک محیطهای پیوستهیافت میشود به شرح زیر است که شامل موارد مرتبط با دما نیستند
طول
|