آکتینیدها
۱۵ عنصر فلزی از اکتینیم (با عدد اتمی ۸۹) تا لورنسیم (با عدد اتمی ۱۰۳) واقع در دورهٔ هفتم جدول تناوبی را اکتینیدها میگویند. این نام از نام عنصر اکتینیم گرفته شدهاست. خواص شیمیایی این عناصر شبیه به عنصر اکتینیم است. همهٔ این عنصرها به جز لورنسیم جزو بلوک اف هستند. لورنسیم جزو بلوک دی است اما خواص شیمیاییاش مشابه با چهاردهتای دیگر است. برعکس عنصرهای لانتانید، تنها چند عنصر اول این ردیف (توریم، پروتاکتینیوم و اورانیوم) در طبیعت یافت میشوند. از عنصر چهارم این سری به بعد که عنصرهای ترانس اورانیوم نام دارند، در طبیعت یافت نمیشوند و همگی رادیواکتیو هستند. در این عنصرها ساختارهسته نسبت به آرایش الکترونی از اهمیت کاربردی بیشتری برخوردار است. همه اکتینیدها هسته ناپایداری دارند، به این علت که ازجمله عنصرهای پرتوزا بهشمار میآیند. شاید مشهورترین اکتینید، اورانیوم باشد که از فروپاشی هسته آن انرژی لازم برای تولید برق در نیروگاهها، زیر دریاییها و ناوهای هواپیمابر فراهم میشود.
| 89Ac | 90Th | 91Pa | 92U | 93Np | 94Pu | 95Am | 96Cm | 97Bk | 98Cf | 99Es | 100Fm | 101Md | 102No | 103Lr |
خواص
| Property | Ac | Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core charge | ۸۹ | ۹۰ | ۹۱ | ۹۲ | ۹۳ | ۹۴ | ۹۵ | ۹۶ | ۹۷ | ۹۸ | ۹۹ | ۱۰۰ | ۱۰۱ | ۱۰۲ | ۱۰۳ |
| جرم اتمی | [۲۲۷] | ۲۳۲٫۰۳۸۱ | ۲۳۱٫۰۳۵۸۸ | ۲۳۸٫۰۲۸۹۱ | [۲۳۷] | [۲۴۴] | [۲۴۳] | [۲۴۷] | [۲۴۷] | [۲۵۱] | [۲۵۲] | [۲۵۷] | [۲۵۸] | [۲۵۹] | [۲۶۲] |
| تعداد ایزوتوپهای طبیعی | ۳ | ۱ | ۲ | ۳ | ۱ | ۲ | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Longest-lived isotope | ۲۲۷ | ۲۳۲ | ۲۳۱ | ۲۳۸ | ۲۳۷ | ۲۴۴ | ۲۴۳ | ۲۴۷ | ۲۴۷ | ۲۵۱ | ۲۵۲ | ۲۵۷ | ۲۵۸ | ۲۵۹ | ۲۶۲ |
| نیمهعمر of the longest-lived isotope | 21.8 years | 14 billion years | ۳۲٬500 years | 4.47 billion years | 2.14 million years | 80.8 million years | ۷٬370 years | 15.6 million years | ۱٬400 years | 900 years | 1.29 years | 100.5 days | 52 days | 58 min | 261 min |
| Electronic configuration in the ground state | 6d17s2 | 6d27s2 | 5f26d17s2or 5f16d27s2 | 5f36d17s2 | 5f46d17s2or 5f57s2 | 5f67s2 | 5f77s2 | 5f76d17s2 | 5f97s2or 5f86d17s2 | 5f107s2 | 5f117s2 | 5f127s2 | 5f137s2 | 5f147s2 | 5f147s27p1 |
| Oxidation state | ۳ | ۳، ۴ | ۳، ۴، ۵ | ۳، ۴، ۵، ۶ | ۳، ۴، ۵، ۶، ۷ | ۳، ۴، ۵، ۶، ۷ | ۲، ۳، ۴ | ۳، ۴ | ۳، ۴ | ۲، ۳ | ۲، ۳ | ۲، ۳ | ۲، ۳ | ۲، ۳ | ۳ |
| Metallic radius, nm | ۰٫۲۰۳ | ۰٫۱۸۰ | ۰٫۱۶۲ | ۰٫۱۵۳ | ۰٫۱۵۰ | ۰٫۱۶۲ | ۰٫۱۷۳ | ۰٫۱۷۴ | ۰٫۱۷۰ | ۰٫۱۸۶ | ۰٫۱۸۶ | — | — | — | — |
| Ionic radius, nm: An4+ An3+ |
— ۰٫۱۲۶ | ۰٫۱۱۴ — | ۰٫۱۰۴ ۰٫۱۱۸ | ۰٫۱۰۳ ۰٫۱۱۸ | ۰٫۱۰۱ ۰٫۱۱۶ | ۰٫۱۰۰ ۰٫۱۱۵ | ۰٫۰۹۹ ۰٫۱۱۴ | ۰٫۰۹۹ ۰٫۱۱۲ | ۰٫۰۹۷ ۰٫۱۱۰ | ۰٫۰۹۶ ۰٫۱۰۹ | ۰٫۰۸۵ ۰٫۰۹۸ | ۰٫۰۸۴ ۰٫۰۹۱ | ۰٫۰۸۴ ۰٫۰۹۰ | ۰٫۰۸۴ ۰٫۰۹۵ | ۰٫۰۸۳ ۰٫۰۸۸ |
| Temperature, °C: melting boiling |
۱۰۵۰ ۳۳۰۰ | ۱۷۵۰ ۴۸۰۰ | ۱۵۷۲ ۴۴۰۰ | ۱۱۳۰ ۳۸۰۰ | ۶۴۰ ۳۹۰۰ | ۶۴۰ ۳۲۳۰ | ۱۱۷۶ ۲۶۱۰ | ۱۳۴۰ — | ۱۰۵۰ — | ۹۰۰ — | ۸۶۰ — | ۱۵۳۰ — | ۸۳۰ — | ۸۳۰ — | ۱۶۳۰ — |
| Density, g/cm3 | ۱۰٫۰۷ | ۱۱٫۷۸ | ۱۵٫۳۷ | ۱۹٫۰۶ | ۲۰٫۲۵ | ۱۹٫۸۴ | ۱۱٫۷ | ۱۳٫۵۱ | ۱۴٫۷۸ | ||||||
| Standard electrode potential, V: E° (An4+/An0) E° (An3+/An0) |
— −۲٫۱۳ | −۱٫۸۳ — | −۱٫۴۷ — | −۱٫۳۸ −۱٫۶۶ | −۱٫۳۰ −۱٫۷۹ | −۱٫۲۵ −۲٫۰۰ | −۰٫۹۰ −۲٫۰۷ | −۰٫۷۵ −۲٫۰۶ | −۰٫۵۵ −۱٫۹۶ | −۰٫۵۹ −۱٫۹۷ | −۰٫۳۶ −۱٫۹۸ | −۰٫۲۹ −۱٫۹۶ | — −۱٫۷۴ | — −۱٫۲۰ | - −۲٫۱۰ |
| Color [M(H2O)n]4+ [M(H2O)n]3+ |
— Colorless | Colorless Blue | Yellow Dark blue | Green Purple | Yellow-green Purple | Brown Violet | Red Rose | Yellow Colorless | نخودی Yellow-green | سبز سبز | — Pink | — — | — — | — — | — — |
| Oxidation state | ۸۹ | ۹۰ | ۹۱ | ۹۲ | ۹۳ | ۹۴ | ۹۵ | ۹۶ | ۹۷ | ۹۸ | ۹۹ |
| +3 | Ac3+ | Th3+ | Pa3+ | U3+ | Np3+ | Pu3+ | Am3+ | Cm3+ | Bk3+ | Cf3+ | Es3+ |
| +4 | Th4+ | Pa4+ | U4+ | Np4+ | Pu4+ | Am4+ | Cm4+ | Bk4+ | Cf4+ | ||
| +۵ | PaO2+ | UO2+ | NpO2+ | PuO2+ | AmO2+ | ||||||
| +۶ | UO22+ | NpO22+ | PuO22+ | AmO22+ | |||||||
| +۷ | NpO23+ | PuO23+ | [AmO6]5- |
- خواص فیزیکی
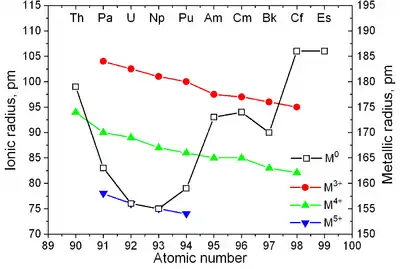 | |
| Major crystal structures of some actinides vs. temperature | Metallic and ionic radii of actinides[2] |


| لانتانیدها | Ln3+، Å | Actinides | An3+، Å | An4+، Å |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| لانتان | ۱٫۰۶۱ | اکتینیم | ۱٫۱۱ | – |
| سریم | ۱٫۰۳۴ | توریم | ۱٫۰۸ | ۰٫۹۹ |
| پرازئودیمیم | ۱٫۰۱۳ | پروتاکتینیم | ۱٫۰۵ | ۰٫۹۳ |
| نئودیمیم | ۰٫۹۹۵ | اورانیم | ۱٫۰۳ | ۰٫۹۳ |
| پرومتیم | ۰٫۹۷۹ | نپتونیوم | ۱٫۰۱ | ۰٫۹۲ |
| ساماریم | ۰٫۹۶۴ | پلوتونیم | ۱٫۰۰ | ۰٫۹۰ |
| یوروپیم | ۰٫۹۵۰ | امریسیم | ۰٫۹۹ | ۰٫۸۹ |
| گادولینیم | ۰٫۹۳۸ | کوریم | ۰٫۹۸ | ۰٫۸۸ |
| تربیم | ۰٫۹۲۳ | برکلیم | - | - |
| دیسپروزیم | ۰٫۹۰۸ | کالیفرنیم | - | - |
| هولمیم | ۰٫۸۹۴ | اینشتینیم | - | - |
| اربیم | ۰٫۸۸۱ | فرمیم | - | - |
| تولیم | ۰٫۸۶۹ | مندلیفیم | - | - |
| ایتربیم | ۰٫۸۵۸ | نوبلیم | - | - |
| لوتتیم | ۰٫۸۴۸ | لارنسیم | - | - |
 Uranyl nitrate (UO2(NO3)2).
Uranyl nitrate (UO2(NO3)2). Aqueous solutions of uranium III, IV, V, VI salts.
Aqueous solutions of uranium III, IV, V, VI salts. Aqueous solutions of neptunium III, IV, V, VI, VII salts.
Aqueous solutions of neptunium III, IV, V, VI, VII salts. Aqueous solutions of plutonium III, V, VI, VII salts.
Aqueous solutions of plutonium III, V, VI, VII salts.

 U3O8 (yellowcake).
U3O8 (yellowcake).
ترکیبها
- اکسیدها و هیدروکسیدها
| ترکیب | رنگ | ساختار شیمیایی، نوع | ثابت شبکه بلوری، Å | چگال، g/cm3 | دما، °C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | |||||
| Ac2O3 | سفید | Hexagonal, La2O3 | ۴٫۰۷ | - | ۶٫۲۹ | ۹٫۱۹ | – |
| PaO2 | - | مکعبی، CaF2 | ۵٫۵۰۵ | - | - | - | - |
| Pa2O5 | سفید | مکعبی، CaF2 مکعبی Tetragonal Hexagonal Rhombohedral Orthorhombic | ۵٫۴۴۶ ۱۰٫۸۹۱ ۵٫۴۲۹ ۳٫۸۱۷ ۵٫۴۲۵ ۶٫۹۲ | - - - - - ۴٫۰۲ | - ۱۰٫۹۹۲ ۵٫۵۰۳ ۱۳٫۲۲ - ۴. ۱۸ | - | ۷۰۰ ۷۰۰–۱۱۰۰ ۱۰۰۰ ۱۰۰۰–۱۲۰۰ ۱۲۴۰–۱۴۰۰ – |
| ThO2 | بیرنگ | مکعبی | ۵٫۵۹ | - | - | ۹٫۸۷ | – |
| UO2 | قهوهای-سیاه | مکعبی | ۵٫۴۷ | - | - | ۱۰٫۹ | – |
| NpO2 | Greenish-قهوهای | مکعبی، CaF2 | ۵٫۴۲۴ | - | - | ۱۱٫۱ | – |
| PuO | سیاه | مکعبی، NaCl | ۴٫۹۶ | - | - | ۱۳٫۹ | – |
| PuO2 | Olive green | مکعبی | ۵٫۳۹ | - | - | ۱۱٫۴۴ | – |
| Am2O3 | Red-brown Red-brown | مکعبی، Mn2O3 Hexagonal, La2O3 | ۱۱٫۰۳ ۳٫۸۱۷ | - | - ۵٫۹۷۱ | ۱۰٫۵۷ ۱۱٫۷ | – |
| AmO2 | Black | مکعبی، CaF2 | ۵٫۳۷۶ | - | - | - | - |
| Cm2O3 | سفید[10] - - | مکعبی، Mn2O2 Hexagonal, LaCl3 Monoclinic, Sm2O3 | ۱۱٫۰۱ ۳٫۸۰ ۱۴٫۲۸ | - - ۳٫۶۵ | - ۶ ۸٫۹ | ۱۱٫۷ | – |
| CmO2 | سیاه | مکعبی، CaF2 | ۵٫۳۷ | - | - | - | - |
| Bk2O3 | قهوهای روشن | مکعبی، Mn2O3 | ۱۰٫۸۸۶ | - | - | - | - |
| BkO2 | قرمز-قهوهای | مکعبی، CaF2 | ۵٫۳۳ | - | - | - | - |
| Cf2O3[11] | Colorless Yellowish - | مکعبی، Mn2O3 Monoclinic, Sm2O3 Hexagonal, La2O3 | ۱۰٫۷۹ ۱۴٫۱۲ ۳٫۷۲ | - ۳٫۵۹ - | - ۸٫۸۰ ۵٫۹۶ | - | - |
| CfO2 | سیاه | مکعبی | ۵٫۳۱ | - | - | - | - |
| Es2O3 | - | مکعبی، Mn2O3 Monoclinic ششگوش، La2O3 | ۱۰٫۰۷ ۱۴٫۱ ۳٫۷ | - ۳٫۵۹ - | - ۸٫۸۰ ۶ | - | - |
| Oxidation state | ۸۹ | ۹۰ | ۹۱ | ۹۲ | ۹۳ | ۹۴ | ۹۵ | ۹۶ | ۹۷ | ۹۸ | ۹۹ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +۳ | Pu2O3 | Am2O3 | Cm2O3 | Bk2O3 | Cf2O3 | Es2O3 | |||||
| +4 | ThO2 | PaO2 | UO2 | NpO2 | PuO2 | AmO2 | CmO2 | BkO2 | CfO2 | ||
| +۵ | PaO2+ | U2O5 | Np2O5 | ||||||||
| +۶ | U3O8 | ||||||||||
| UO3 |
| فرمول شیمیایی | ThO2 | PaO2 | UO2 | NpO2 | PuO2 | AmO2 | CmO2 | BkO2 | CfO2 |
| شماره ثبت سیایاس | ۱۳۱۴-۲۰-۱ | ۱۲۰۳۶-۰۳-۲ | ۱۳۴۴-۵۷-۶ | ۱۲۰۳۵-۷۹-۹ | ۱۲۰۵۹-۹۵-۹ | ۱۲۰۰۵-۶۷-۳ | ۱۲۰۱۶-۶۷-۰ | ۱۲۰۱۰-۸۴-۳ | ۱۲۰۱۵-۱۰-۰ |
| PubChem | 14808 | ۱۰۹۱۶ | |||||||
| جرم مولی | ۲۶۴٫۰۴ | ۲۶۳٫۰۳۵ | ۲۷۰٫۰۳ | ۲۶۹٫۰۴۷ | ۲۷۶٫۰۶۳ | ۲۷۵٫۰۶ | ۲۷۰–۲۸۴** | ۲۷۹٫۰۶۹ | ۲۸۳٫۰۷۸ |
| نقطه ذوب | ۳۳۹۰ °C | ۲۸۷۸ °C | 2600 °C | 2400 °C | 2050 °C | ||||
| نقطه جوش | ۴۴۰۰ °C | ۲۸۰۰ °C | |||||||
| ساختار | 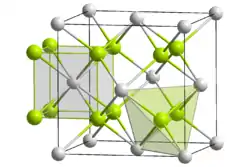 An4+: __ / O2−: __ | ||||||||
| گروه فضایی | Fm۳m | ||||||||
| عدد کوئوردیناسیون | An[8], O[4] | ||||||||
- An – اکتینید
**بسته به ایزوتوپها
- نمکها
| فرمول شیمیایی | AcCl3 | UCl3 | NpCl3 | PuCl3 | AmCl3 | CmCl3 | BkCl3 | CfCl3 |
| شماره ثبت سیایاس | ۲۲۹۸۶-۵۴-۵ | ۱۰۰۲۵-۹۳-۱ | ۲۰۷۳۷-۰۶-۸ | ۱۳۵۶۹-۶۲-۵ | ۱۳۴۶۴-۴۶-۵ | ۱۳۵۳۷-۲۰-۷ | ۱۳۵۳۶-۴۶-۴ | ۱۳۵۳۶-۹۰-۸ |
| PubChem | ۱۶۷۴۴۴ | |||||||
| جرم مولی | ۳۳۳٫۳۸۶ | ۳۴۴٫۳۸۷ | ۳۴۳٫۴۰۶ | ۳۵۰٫۳۲ | ۳۴۹٫۴۲ | ۳۴۴–۳۵۸** | ۳۵۳٫۴۲۸ | ۳۵۷٫۴۳۸ |
| نقطه ذوب | ۸۳۷ °C | 800 °C | 767 °C | 715 °C | 695 °C | 603 °C | 545 °C | |
| نقطه جوش | ۱۶۵۷ °C | ۱۷۶۷ °C | 850 °C | |||||
ساختار بلوری| Colspan = "8"|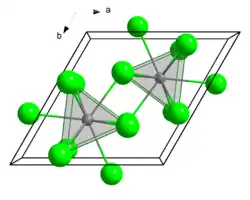 An3+: __ / Cl−: __ | ||||||||
| گروه فضایی | P63/m | |||||||
| عدد کوئوردیناسیون | An*[9], Cl [۳] | |||||||
| ثابت شبکه بلوری | a = ۷۶۲ pm c = 455 pm | a = 745.2 pm c = 432.8 pm | a = 739.4 pm c = 424.3 pm | a = 738.2 pm c = 421.4 pm | a = 726 pm c = 414 pm | a = 738.2 pm c = 412.7 pm | a = 738 pm c = 409 pm | |
- *An – اکتینید
**بسته به ایزوتوپها
| ترکیب | رنگ | ساختار بلوری، نوع | ثابت شبکه بلوری، Å | چگالی، g/cm3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | ||||
| AcF3 | سفید | Hexagonal, LaF3 | ۴٫۲۷ | - | ۷٫۵۳ | ۷٫۸۸ |
| PaF4 | Dark brown | دستگاه بلوری مونوکلینیک | ۱۲٫۷ | ۱۰٫۷ | ۸٫۴۲ | – |
| PaF5 | Black | دستگاه بلوری تتراگونال، β-UF5 | ۱۱٫۵۳ | - | ۵٫۱۹ | – |
| ThF4 | Colorless | Monoclinic | ۱۳ | ۱۰٫۹۹ | ۸٫۵۸ | ۵٫۷۱ |
| UF3 | Reddish-purple | Hexagonal | ۷٫۱۸ | - | ۷٫۳۴ | ۸٫۵۴ |
| UF4 | Green | Monoclinic | ۱۱٫۲۷ | ۱۰٫۷۵ | ۸٫۴۰ | ۶٫۷۲ |
| α-UF5 | Bluish | Tetragonal | ۶٫۵۲ | - | ۴٫۴۷ | ۵٫۸۱ |
| β-UF5 | Bluish | Tetragonal | ۱۱٫۴۷ | - | ۵٫۲۰ | ۶٫۴۵ |
| UF6 | Yellowish | Orthorhombic | ۹٫۹۲ | ۸٫۹۵ | ۵٫۱۹ | ۵٫۰۶ |
| NpF3 | Black or purple | Hexagonal | ۷٫۱۲۹ | - | ۷٫۲۸۸ | ۹٫۱۲ |
| NpF4 | Light green | Monoclinic | ۱۲٫۶۷ | ۱۰٫۶۲ | ۸٫۴۱ | ۶٫۸ |
| NpF6 | Orange | Orthorhombic | ۹٫۹۱ | ۸٫۹۷ | ۵٫۲۱ | ۵ |
| PuF3 | Violet-blue | Trigonal | ۷٫۰۹ | - | ۷٫۲۵ | ۹٫۳۲ |
| PuF4 | Pale brown | Monoclinic | ۱۲٫۵۹ | ۱۰٫۵۷ | ۸٫۲۸ | ۶٫۹۶ |
| PuF6 | Red-brown | Orthorhombic | ۹٫۹۵ | ۹٫۰۲ | ۳٫۲۶ | ۴٫۸۶ |
| AmF3 | Pink or light نخودی | hexagonal, LaF3 | 7.04[16][17] | - | ۷٫۲۵۵ | ۹٫۵۳ |
| AmF4 | Orange-red | دستگاه بلوری مونوکلینیک | ۱۲٫۵۳ | ۱۰٫۵۱ | ۸٫۲۰ | – |
| CmF3 | قهوهای تا سفید | Hexagonal | ۴٫۰۴۱ | - | ۷٫۱۷۹ | ۹٫۷ |
| CmF4 | Yellow | Monoclinic, UF4 | ۱۲٫۵۱ | ۱۰٫۵۱ | ۸٫۲۰ | – |
| BkF3 | Yellow-green | دستگاه بلوری لوزیپهلو، LaF3 دستگاه بلوری اورتورومبیک، YF3 | ۶٫۹۷ ۶٫۷ | - ۷٫۰۹ | ۷٫۱۴ ۴٫۴۱ | ۱۰٫۱۵ ۹٫۷ |
| BkF4 | - | Monoclinic, UF4 | ۱۲٫۴۷ | ۱۰٫۵۸ | ۸٫۱۷ | – |
| CfF3 | - - | Trigonal, LaF3 Orthorhombic, YF3 | ۶. ۹۴ ۶٫۶۵ | - ۷٫۰۴ | ۷٫۱۰ ۴٫۳۹ | – |
| CfF4 | - - | Monoclinic, UF4 Monoclinic, UF4 | ۱٫۲۴۲ ۱٫۲۳۳ | ۱٫۰۴۷ ۱٫۰۴۰ | ۸٫۱۲۶ ۸٫۱۱۳ | – |

جستارهای وابسته
منابع
- Yu.D. Tretyakov, ed. (2007). Non-organic chemistry in three volumes. Chemistry of transition elements. 3. Moscow: Academy. ISBN 5-7695-2533-9.
- Greenwood, p. 1263
- Greenwood, p. 1265
- Myasoedov, pp. 30–31
- Z. K. Karalova, B. Myasoedov (1982). Actinium. Analytical chemistry items. Moscow: Nauka.
- V.A. Mikhailov, ed. (1971). Analytical chemistry of neptunium. Moscow: Nauka.
- E.S. Palshin (1968). Analytical chemistry of protactinium. Moscow: Nauka. Unknown parameter
|author-separator=ignored (help) - Myasoedov, p. 88
- "Таблица Inorganic and Coordination compounds" (به Russian). Retrieved 2010-07-11. Unknown parameter
|description=ignored (help) - According to other sources, cubic sesquioxide of curium is olive-green. See "Соединения curium site XuMuK.ru" (به Russian). Retrieved 2010-07-11.
- The atmosphere during the synthesis affects the lattice parameters, which might be due to non-stoichiometry as a result of oxidation or reduction of the trivalent californium. Main form is the cubic oxide of californium(III).
- Greenwood, p. 1268
- "Information from webelements.com".
- Greenwood, p. 1270
- Myasoedov, pp. 96–99
- F. Weigel; J. Katz; G. Seaborg (1997). The Chemistry of the Actinide Elements. 2. Moscow: Mir. ISBN 5-03-001885-9. Unknown parameter
|author-separator=ignored (help) - Nave, S.; Haire, R.; Huray, Paul (1983). "Magnetic properties of actinide elements having the 5f^{6} and 5f^{7} electronic configurations". Physical Review B. 28: 2317. Bibcode:1983PhRvB..28.2317N. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.28.2317.
- Wikipedia contributors, "Actinide," Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, https://secure.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/w/index.php?title=Actinide&oldid=447118919 (accessed September 2, 2011).
- دانشنامه رشد
