جدول زمانی اختراعها در ایالات متحده آمریکا (۱۹۴۶–۱۹۹۱)
جدول زمانی اختراعها در ایالات متحده (۱۹۴۶–۱۹۹۱)، تعدادی از مهمترین اختراعات و ابداعات شکل گرفته توسط شهروندان ایالات متحده آمریکا، از ۱۹۴۶ تا ۱۹۹۱ میلادی است. این اختراعات در بازهٔ زمانی جنگ سرد قرار دارد که تا فروپاشی اتحاد جماهیر شوروی ادامه مییابد. اختراعات به دلیل بند ۸ از بخش هشتم ماده اول قانون اساسی آمریکا شامل حق ثبت و حقوق مالکیت میشوند.
| « | به منظور تشویق به پیشرفت علم و هنرهای مفید، از طریق ایجاد سازوکارهای اطمینانبخش و برای مدت زمانی تعیین شده به نویسندگان و مخترعان، حق انحصاری برای تالیفات و اکتشافات، نوآوریها و اختراعات را میدهد. | » |
این حق در سال ۱۷۹۰ پس از تصویب کنگره به امضای رئیس جمهور جورج واشنگتن رسید که در ادامه به تأسیس اداره ثبت اختراع منجر شد. با این حال این روند در سال ۱۸۳۶ دچار تکامل شد و منجر به تشکیل اداره ثبت اختراع و نشان تجاری ایالات متحده شد. از زمان تشکیل این اداره در سال ۱۸۳۶ تا سال ۲۰۱۱، در مجموع ۷٬۸۶۱٬۳۱۷ اختراع به ثبت رسیدهاست.
جنگ سرد (۱۹۴۶–۱۹۹۱)
(۱۹۴۶–۱۹۴۹) سالهای نخستین پس از پایان جنگ








۱۹۴۶ تلسکوپ فضایی (لایمن اسپیتزر)[1]
۱۹۴۶ تاپرور (ارل سیلاس توپر)[2]
۱۹۴۷ ترانزیستور (جان باردین و والتر هاوسر براتین)[4]
۱۹۴۷ اکریلیک (لئونارد بوکر و سم گلدن)[7]
۱۹۴۸ بادسواری (نیومن داربی)[8]
۱۹۴۸ تلویزیون کابلی (جان و مارگارت والسون)[9]
۱۹۴۸ بازی ویدئویی (توماس تی گولداسمیت)[10]
۱۹۴۹ تاریخگذاری رادیوکربن (ویلارد لیبای)[11]
۱۹۴۹ یخ پرداز (فرانک زامبونی)[12]
۱۹۴۹ الکتروکاردیوگرام دینامیک (نورمن هولتر)[14]
۱۹۴۹ آدمک آزمایش تصادف (ساموئل دابلیو. آلدرسون)[15][16]
۱۹۴۹ مترجم رایانهای (گریس هاپر)[17]
دهه ۱۹۵۰
۱۹۵۰ کد همینگ (ریچارد همینگ)[19]
۱۹۵۰ اتوکیو (هابرت شلافلی)[20]
۱۹۵۱ استلراتور (لایمن اسپیتزر)[21]
۱۹۵۲ کیسه هوا (جان دابلیو. هاتریک)[22]
۱۹۵۲ بارکد (نورمن وودلند)[23]
۱۹۵۲ قلب مصنوعی (فورست دیوای دادریل)[24]
۱۹۵۳ بایپس قلبی ریوی (جان هیشام گیبون)[25]
۱۹۵۳ ماژیک (سیدنی راسنتال)[27]
۱۹۵۳ قفل چرخ (فرانک ماروگ)[28]
۱۹۵۳ میزر (چارلز هارد تاونز، جی. پی. گورودن و اچ. جی زیگر)[29]
۱۹۵۴ احیای قلبی ریوی (جیمز ایلم)[30]
۱۹۵۵ زیردریایی هستهای (هیمن ریکور)[31]
۱۹۵۵ هارد دیسک (رینولد جانسون)[32]
۱۹۵۶ پرزگیر (نیکولاس مککای)[33]
۱۹۵۶ روبات صنعتی (جرج دوول و جو انگلبرگر)[35]
۱۹۵۶ سیستمعامل (اون موک و باب پاتریک)[36]
۱۹۵۷ دوربین گاما (هل انگر)[39]
۱۹۵۸ لیسپ (جان مککارتی)[40]
۱۹۵۸ مدار مجتمع (جک کیلبی)[41]
۱۹۵۹ ماهواره هواشناسی[42]
دهه ۱۹۶۰











۱۹۶۰ چمن مصنوعی (رلیانت آسترودام)[43]
۱۹۶۰ کارت مغناطیسی (فورست پری)[44]
۱۹۶۰ سامانه ماهوارهای ناوبری جهانی[44]
۱۹۶۰ قرص ضد بارداری خوراکی (جورج پینکاس)[45]
۱۹۶۰ لیزر گازی (ویلیام آر بنت، دان هریوت و علی جوان)[46]
۱۹۶۱ صفحه گسترده (باب فرانکستون)[47][48]
۱۹۶۱ رایانه پوشیدنی (کلود شانون)[49]
۱۹۶۱ پسخوراند زیستی (نیل میلر)[50]
۱۹۶۲ ماهواره مخابراتی (جان رابینسون پیرس)[51]
۱۹۶۲ LED (نیک هالنیاک)[53][54]
۱۹۶۲ لیزر دیودی (رابرت ان. هال)[55]
۱۹۶۲ گلوکومتر (لیلاند کلارک)[56]
۱۹۶۳ ماوس (داگلاس انگلبارت)[57]
۱۹۶۳ زبان برنامهنویسی بیسیک (جان جی. کمنی و توماس یوجین کورتز)[58]
۱۹۶۴ نمایشگر پلاسما (دونالد بیتزر)[59][60]
۱۹۶۴ السیدی (جورج اچ. هیلمر)[61]
۱۹۶۵ اسنوبرد سواری (شرمن پاپن)[62]
۱۹۶۵ کولار (استفانی کولک)[63]
۱۹۶۵ ابرمتن (تئودور هولم نلسون)[64]
۱۹۶۵ تلفنهای بیسیم (جورج سویگرت)[65]
۱۹۶۵ قلم فضایی (پل سی. فیشر)[66]
۱۹۶۵ رایانه کوچک (چارلز مولنر)[67]
۱۹۶۵ لوح فشرده (جیمز راسل)[68]
۱۹۶۶ حافظه دسترسی تصادفی پویا (رابرت دنارد)[69]
۱۹۶۷ ماشین حساب (جک کیلبی)[71]
۱۹۶۸ واقعیت مجازی (ایوان سادرلند)[72]
۱۹۶۹ چاپگر لیزری (گری استارکودر)[75]
۱۹۶۹ هواپیمای پهنپیکر (جو ساتر)[76]
۱۹۶۹ زبان نشانهگذاری (چارلز گلدفارب)[77]
دهه ۱۹۷۰

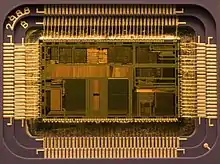





۱۹۷۰ شبکه محلی بیسیم (نورمن آبرامسون)[78]
۱۹۷۰ تخته موجسواری (جک اونیل)[79]
۱۹۷۱ رایانه شخصی (جان بلنکنبیکر)[80][81]
۱۹۷۱ ریزپردازنده (مرسین هاف، فدریکو فاگین و استنلی میزور)[82]
۱۹۷۱ فلاپیدیسک (دیوید ال. نوبل)[83]
۱۹۷۱ رایانامه (ایمیل) (ری تاملینسون)[85]
۱۹۷۲ زبان برنامهنویسی C (دنیس ریچی)[86]
۱۹۷۲ کنسول بازی (رالف اچ. بائر)[87]
۱۹۷۲ سامانه موقعیتیاب جهانی (GPS) (بردفورد پارکینسون، مل برنبام، باب رنارد، جیم اسپیلکر و ریچارد ایستون)[88]
۱۹۷۲ برشنگاری با گسیل پوزیترون (ادوارد جی. هافمن)[89]
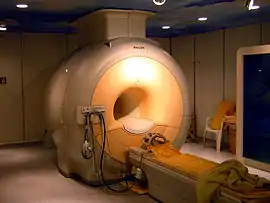
۱۹۷۲ MRI (ریموند دامادیان)[90]
۱۹۷۳ جتاسکی (کلایتون یاکوبسون)[91]
۱۹۷۳ کاغذ الکترونیک (نیک شرایدون)[92]
۱۹۷۳ DNA نوترکیب (استنلی نورمن کوهن و هربرت بویر)[93]
۱۹۷۳ مبدل کاتالیست (جان جی. مانی و کارل دی. کیث)[94]
۱۹۷۳ تلفن همراه (داگلاس اچ. رینگ، دابلیو. ری یانگ، مارتین کوپر و ژوئل اس. انجل)[95]
۱۹۷۳ ایمیل صوتی (توماس جی. واتسون)[96]
۱۹۷۵ دوربین دیجیتال (استیون ساسون در ایستمن کداک)[97][98]
۱۹۷۵ اترنت (رابرت متکالف)[99]
۱۹۷۸ بیبیاس (وارد کریستنسن)[100]
دهه ۱۹۸۰ و اوایل دهه ۱۹۹۰

۱۹۸۱ کنترل-آلت-دیلیت (دیوید بردلی)[103]
۱۹۸۱ شاتل فضایی[104]
۱۹۸۱ پینتبال (هایس نوئل، باب گارنسی و چارلز گینز)[105]
۱۹۸۱ واسط گرافیکی کاربر (الن کی و داگلاس انگلبارت)[106]
۱۹۸۴ واکنش زنجیرهای پلیمراز (کری مالیس)[109]
۱۹۸۶ میکروسکوپ نیروی اتمی (کریستوف گربر، گرد بینینگ و کالوین کویت)[110]
۱۹۸۶ استریولیتوگرافی (چاک هال)[111]
۱۹۸۷ زبان برنامهنویسی پرل (لری وال)[112]
۱۹۸۸ مدلسازی تهنشین جوشخورده (اس. اسکات کرامپ)[113]
۱۹۸۸ تیسیال (جان استرهات)[114]
۱۹۸۸ چسب نیکوتین (موری یرویک)[115]
۱۹۸۸ فایروال (ویلیام چیزویک و استیون بلوین)[116]
۱۹۸۹ فرمت فایل ZIP (فیل کاتز)[117]
۱۹۹۰ لامپ گوگردی (مایکل اوری).[118]
۱۹۹۱ مورچه رباتیک (جیمز مکلورکین)[119]
جستارهای وابسته
منابع
- "Hubble Essentials: About Lyman Spitzer, Jr". Hubble Site.
- "Earl S. Tupper (1907–1983)". Syracuse University Library. Archived from the original on 19 September 2011. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "Marion Donovan, 81, Solver Of the Damp-Diaper Problem". New York City Times. November 18, 1998.
- "November 17 – December 23, 1947: Invention of the First Transistor". American Physical Society.
- "History of Defibrillation". ADI Media Private Limited.
- "Testing The First Supersonic Aircraft". NASA. Archived from the original on 12 April 2010. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "A History of GOLDEN Artist Colors, Inc". Golden Artist Colors, Inc.
- "A Chronological Order Of The Development Of The Free Sail System Sailboard". The Hart's Homepage.
- "Cable TV: From Community Antennas to Wired Cities". Harvard Business School.
- "The First Video Game?". Brookhaven National Laboratory.
- "Carbon Dating". Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- "The Zamboni Story: Ice Resurfacing". Frank J. Zamboni & Co. Inc. Archived from the original on 4 March 2010. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "The "Atomic Age" of Time Standards". National Institute of Standards and Technology.
- "What are Holter, Event and Transtelephonic Monitors?". American Heart Association.
- "Roswell". Paul V. Galvin Library. Archived from the original on 29 May 2015. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "Evaluation of the Sierra Company Lightweight Helmet" (PDF). Defense Technical Information Center.
- "Grace Hopper". Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- "Leaf Blowers". Portland Leaf Blowers. Archived from the original on 12 August 2008. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "Richard Wesley Hamming". University of St. Andrews.
- "Teleprompter inventor Hubert Schlafly dies at 91". British Broadcasting Corporation. April 27, 2011.
- "Lyman Spitzer: Space telescope pioneer". European Space Agency. Archived from the original on 6 March 2012. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "Airbags". Bryant University. Archived from the original on 5 July 2010. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "A Short History Of Bar Code". Adams Communications.
- "1952: The First Mechanical Heart Pump". General Motors Corporation.
- "Heart-Lung Machine". Invent Now. Archived from the original on 6 December 2010. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "ANDREW F. KAY '40: Building Quality in Computers and Work Flow". Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Archived from the original on 2 November 2011. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- Palm, Kristin (1995). "Marker". CBS Interactive Inc. Archived from the original on 8 July 2012. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "Happy Birthday Denver Boot!r". The Expired Meter.
- "Invention of the Maser and Laser". The American Physical Society.
- "History Of CPR". United States Mine Rescue Association.
- "USS NAUTILUS (SSN-571)". Sub Guru.
- "Reynold Johnson". Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- "Evercare Celebrates 50th Birthday and Golden Anniversary of Its Invention of The Lint Rolle". The Evercare Company. Archived from the original on 25 October 2011. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "Karting's Golden Summer". Crain Communications, Inc. Archived from the original on 18 March 2012. Retrieved 2 October 2019.
- "George C Devol". Encyclopaedia Britannica.
- "History of operating systems". OS Data.
- "Fortran". Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- "Laser". Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- Reports, Wire (November 15, 2005). "Hal Anger, 85; Inventor of Gamma Camera Used in Nuclear Medicine". LA Times. Retrieved May 25, 2010.
- "50th birthday of Lisp (October 1958)". Artificial Intelligence Research Institute. Archived from the original on 20 January 2013. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "Jack Kilby: The Chip that Jack Built". Texas Instruments.
- "A Complete Picture: Weather Satellites and Contemporary Meteorology" (PDF). National Weather Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 March 2009. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "Artificial Turf". Purchase Green. Archived from the original on 6 December 2010. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "CSCI 321- Software Project School of Information Technology & Computer Science" (PDF). University of Wollongong. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 July 2011. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "Gregory Pincus, Father of the Pill". Population Reference Bureau. Archived from the original on 16 May 2013. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- Gray, Sadie (August 6, 2008). "Professor William Bennett: co-inventor of the gas laser". London: The Times. Retrieved March 26, 2010.
- "A Brief History of Spreadsheets". Decision Support Systems Resources.
- "Dan Bricklin, Co-Inventor of the Spreadsheet, Discusses How Nerds Are Like Sports Stars". The New York Observer.
- "Edward O. Thorpe". Edward Thorpe.
- Nagourney, Eric (April 2, 2002). "Neal E. Miller Is Dead at 92; Studied Brain and Behavior". The New York Times.
- "Communications Satellite". National Inventors Hall of Fame Foundation, Inc. Archived from the original on 5 December 2010. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "AUTOMATIC DUMP TYPE CHARCOAL LIGHTER". United States Patent and Trademark Office.
- "Nick Holonyak". Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- "Nick Holonyak honored for inventing the LED". LEDs Magazine. Archived from the original on 20 January 2013. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "Semiconductor injection laser". Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- "Diabetes: Glucose Sensors and Drug Delivery" (PDF). McMaster University. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 February 2006. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "1963: Douglas Engelbart Invents the Mouse". University of California at Berkeley. Archived from the original on 27 July 2010. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "John G. Kemeny: BASIC and DTSS: Everyone a Programmer". Columbia Univ.
- "Dr. Donald Bitzer Co-Inventor, Plasma Display". Consumer Electronics Association. Archived from the original on 15 August 2011. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "H. Gene Slottow Co-inventor, Plasma Display". Consumer Electronics Association. Archived from the original on 14 August 2011. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "Liquid Crystal Display Dynamic Scattering Method". Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- "THE HISTORY OF SNOWBOARDING". Bulgarian Ski.
- "Inventor of Kevlar". Famous Women Inventors.
- "Visionary lays into the web". BBC News. October 8, 2001. Retrieved March 26, 2010.
- "'Giving women tech know-how'". BBC News. November 3, 2006. Retrieved March 26, 2010.
- "History of the Fisher Space Pen". Allwrite B.V.
- "DEC PDP-8 minicomputer". UvA Computer Museum.
- "The Little-known Story Of Optical Digital Storage". Northwest Science and Technology.
- "DRAM". Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- "Innovations". Lowepro. Archived from the original on 30 June 2013. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "Calculator History- Invention of the Hand-held Calculator". The Great Idea Finder. Archived from the original on 24 July 2013. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "A Brief History of Virtual Reality". University of Calgary.
- Saslow, Linda (July 18, 1999). "..The Man Whose Stuff Is Still on the Moon". The NEw York Times.
- "Father of the Lunar Module Thomas Kelly Dies". Space.com. Archived from the original on 6 June 2002. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "Gary Starkweather – Laser Printer Inventor". United Business Media LLC. Archived from the original on 11 May 2010. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- "Father knows best". Boeing Commercial Airplanes.
- Encyclopedia of New Media: An Essential Reference to Communication and Technology. The Moshovitis Group. 2003. ISBN 978-0-7619-2382-4.
- "IEEE History Center: Norman Abramson". IEEE.
- The Encyclopedia of Surfing. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt.
- "Timeline of Computer History". Computer History Museum.
- Transforming Global Information and Communication Markets: The Political Economy of Innovation. MIT Press. p. 270.
- "25th Anniversary for Microprocessor". Toronto Star.
- "1971: IBM fashions the floppy". CNN. June 17, 1999. Retrieved May 25, 2010.
- Bebop to the boolean boogie: an unconventional guide to electronics. Newnes.
- "A Conversation With The Inventor Of Email". Jupitermedia Corporation.
- "C – the Programming Language". BBC h2g2.
- "Magnavox Odyssey First home video game console". David Winter.
- Fundamentals of global positioning system receivers: a software approach. John Wiley and Sons.
- "Edward J. Hoffman, UCLA Professor and Co-Inventor of the PET Scanner, Dies at 62". UCLA. Archived from the original on 20 January 2013. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- "Apparatus And Method For Detectin Cancer In Tissue". United States Patent and Trademark Office.
- "PERSONAL WATERCRAFT". Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- "E-paper History: An Interview with Nick Sheridon, Father of E-paper". The Future of Things. Archived from the original on 25 December 2010. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- "Stan Cohen and Herb Boyer "invented" recombinant DNA technology". DNA Learning Center.
- Gray, Sadie (November 21, 2008). "Carl Keith: Research chemist who co-invented the catalytic converter". London: The Times. Retrieved March 26, 2010.
- "Inventor of cell phone: We knew someday everybody would have one". CNN.
- "Human Factors Challenges In Creating a Principal Support Office System The Speech Filing System Approach" (PDF). IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Center. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 January 2013. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- The Visual Dictionary of Photography. AVA Publishing.
- "Steven Sasson named to CE Hall of Fame". Let's Go Digital.
- "Ethernet". University of Aberdeen.
- "Smart Computing Encyclopedia". Sandhills Publishing Company.
- "Winglets". NASA.
- "Polar Fleece". Stitch n Save. Archived from the original on 5 May 2014. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- "Control-Alt-Delete". Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- "The Space Shuttle's First Flight: STS-1". NASA.
- "Splat attack". BBC.
- "A History of the GUI". Condé Nast Digital, Inc.
- "Computing History, 1981–1985: The Internet" (PDF). Computing Networking Services. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 May 2014. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- "A Brief History of the Internet". University System of Georgia.
- "Kary Mullis – biography". KaryMullis.com. Archived from the original on 19 January 2008. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- Methods in Modern Biophysics. Springer.
- "Introduction to StereoLithography Apparatus (SLA)". Rapid Product Development Resource Centre. Archived from the original on 4 October 2008. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- "Beginner's Introduction to Perl(part 1)". Perl.com.
- "Highlights of Fused Deposition Modeling". Engineering Fundamentals.
- "History of Tcl". John Ousterhout. Archived from the original on 6 July 2010. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- Weber, Bruce (May 13, 2008). "Murray Jarvik, 84, Whose Research Helped Lead to Nicotine Patch, Dies". New York Times. Retrieved May 25, 2010.
- "One Size Does Not Fit All: Tailoring Protection with Data Proximate Security". Techworld. Archived from the original on 10 October 2007. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- "Philip K. Katz". Biographies Pioneers of computing A-J.
- "20th Century Inventors: Sulfur Lamp". Smithsonian Institution.
- "James McLurkin". Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
پیوند به بیرون
- American Inventors
- Google: U.S. Patents Search
- PBS: They Made America
- MIT: Invention Dimension
- NASA: Scientific and Technical Information: NASA Spinoff بایگانیشده در ۴ آوریل ۲۰۱۲ توسط Wayback Machine
- National Inventors Hall of Fame Foundation
- The Great Idea Finder
- United States Patent and Trademark Office
